Japan’s Healthcare Expenditures Reach Record High
Economy Health Politics- English
- 日本語
- 简体字
- 繁體字
- Français
- Español
- العربية
- Русский
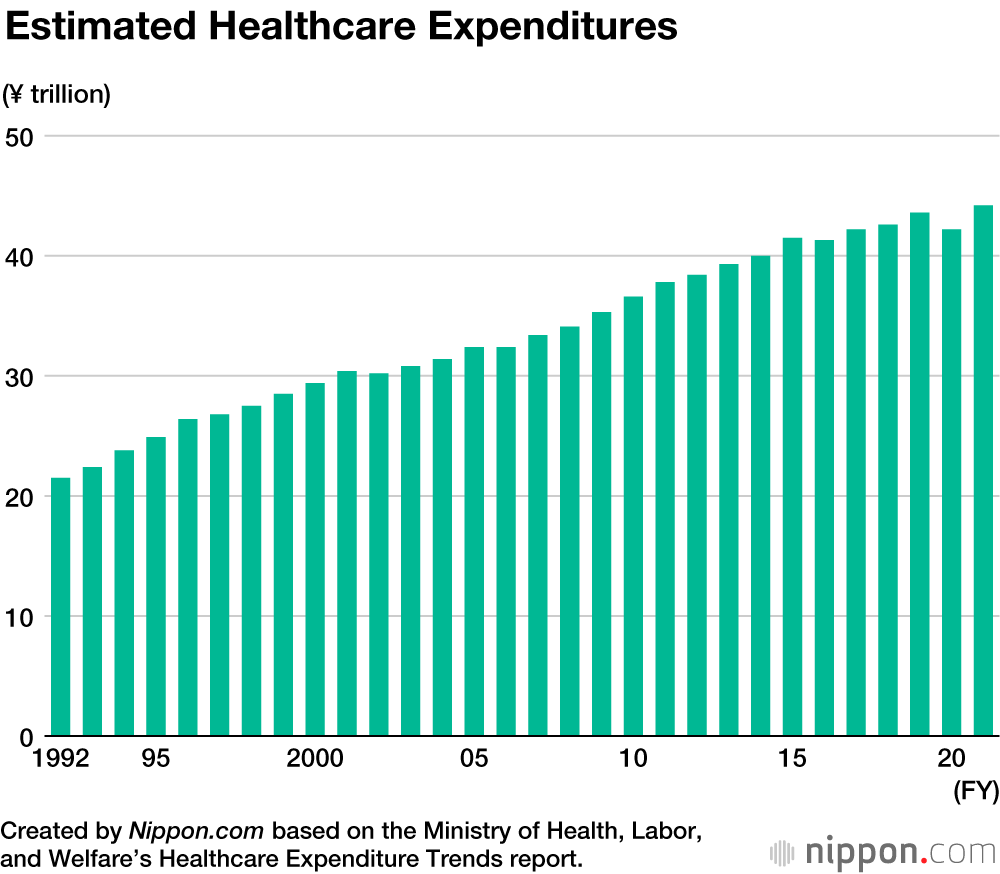
Estimated healthcare expenditures paid to medical institutions in fiscal 2021 reached a record ¥44.2 trillion, an increase of ¥2.0 trillion, or 4.6%, compared to the previous year. Hospitalization increased by 2.8% to ¥17.6 trillion, while outpatient services, home visits, and other medical treatments not involving hospitalization rose by 7.5% to ¥15.3 trillion. Meanwhile, expenditures on prescription medication and dental services grew by 2.7% and 4.8%, respectively.
In fiscal 2020, healthcare expenditures declined as fewer people consulted doctors amid the COVID-19 pandemic. This reluctance to visit the doctor continued in fiscal 2021 as the total number of patients and total consultation days rose just 3.3% year on year, remaining 5.5% lower than in fiscal 2019 just prior to the pandemic. Reasons for the increased expenditures in fiscal 2021 include Japan’s aging population and growing sophistication of medical technologies as well as increased spending on PCR tests and other procedures related to COVID-19.
Average medical expenses per capita increased ¥17,000 year on year to ¥352,000. The median outlay for people under 75 was ¥235,000, but quadrupled to ¥939,000 for those 75 and older.
These preliminary figures represent 98% of officially confirmed healthcare expenditures from the previous year, excluding healthcare outlays related to occupational injuries and cases where patients bore the full cost of medical treatment. Expenditures are expected to continue to increase as the bulk of baby boomers reach advanced old age and the use of more advanced medical technologies grows.
(Translated from Japanese. Banner photo © Pixta.)