Japanese Researchers Feature Regularly Among Ig Nobel Prizewinners
World Science- English
- 日本語
- 简体字
- 繁體字
- Français
- Español
- العربية
- Русский
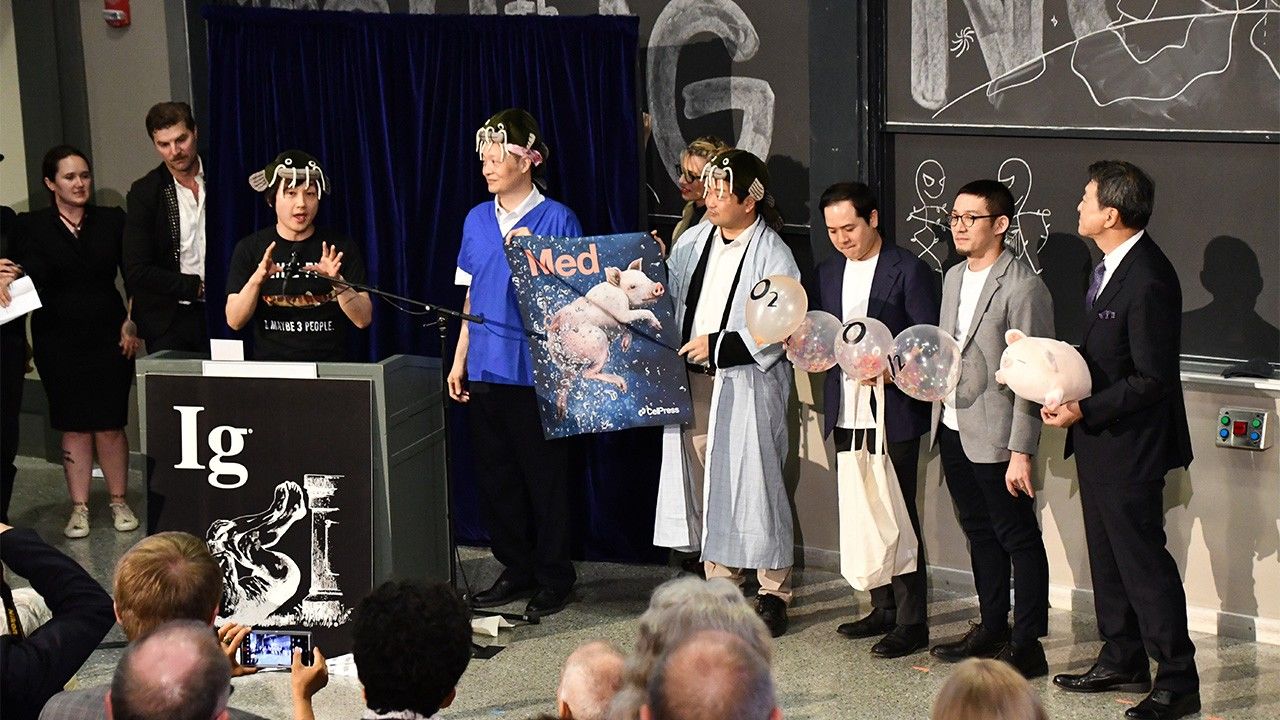
The 2024 Ig Nobel Prize ceremony was held on September 12 at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology. Once again, a Japanese national was among the winners of this prize that makes people laugh and then think. It is the eighteenth straight year since 2007 that Japanese researchers have received an Ig Nobel Prize.
This year, a group led by Takebe Takanori, a professor at Tokyo Medical and Dental University, received the Ig Nobel Prize in Physiology for the discovery that mammals can breathe through the anus by using their intestines.
The Ig Nobel Prize was launched as a parody of the Nobel Prize in 1991 by Annals of Improbable Research, a US scientific humor magazine. The naming is of course a pun on the word “ignoble”, meaning being of low character or having a lack of honor.
The first Japanese prizewinner came in 1992, when a Shiseidō research team led by Kanda Fujihiro won for identifying the chemical compounds that cause foot odor. Nakagaki Toshiyuki, who studies single-celled organisms known as slime molds, has received the prize twice; once in cognitive science in 2008 and a second in transportation planning in 2010.
While many of Japan’s awards have been in science, one came in economics in 1997 for the Tamagotchi. It has also won two awards for peace: in 2002 for developing the Bowlingual dog bark translator, and in 2004 for karaoke.
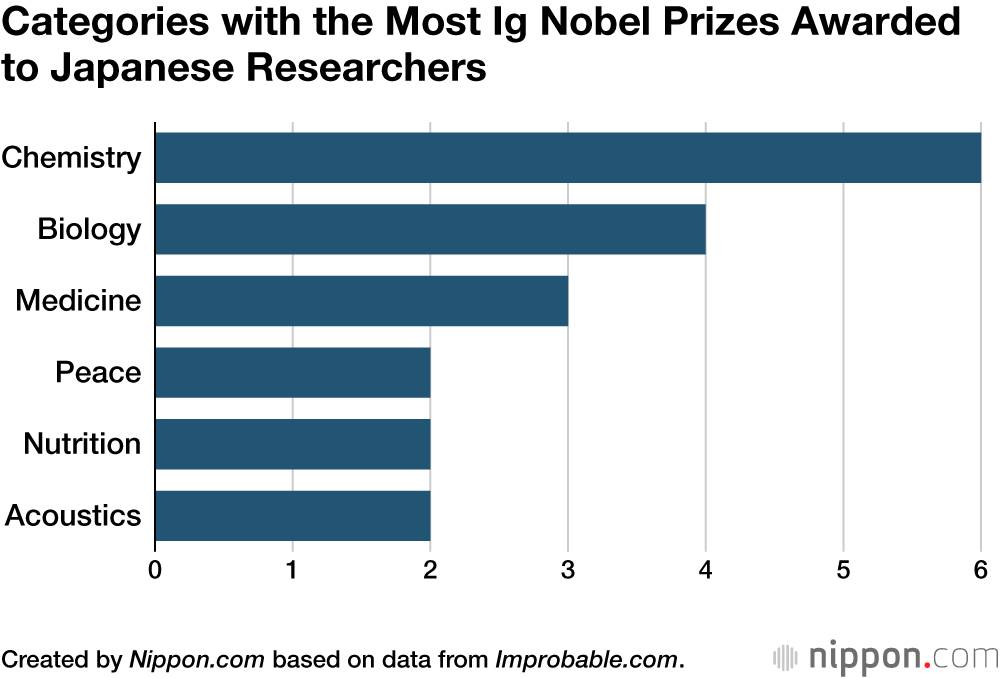
Japanese researchers have received the most prizes in chemistry, with six, followed by four in biology and three in medicine.
Japanese winners of the Ig Nobel Prize are listed below. In many cases, they shared the prize with people of other nationalities.
Japanese Ig Nobel Prizewinners
2024
Physiology
- Takebe Takanori and others
- For discovering that many mammals are capable of breathing through their anus.
2023
Nutrition
- Miyashita Hōmei and Nakamura Hiromi
- For experiments to determine how electrified chopsticks and drinking straws can change the taste of food.
2022
Engineering
- Matsuzaki Gen and others
- For trying to discover the most efficient way for people to use their fingers when turning a knob.
2021
Kinetics
- Murakami Hisashi, Nishinari Katsuhiro, and Nishiyama Yūta
- For conducting experiments to learn why pedestrians sometimes collide with other pedestrians.
2020
Acoustics
- Nishimura Takeshi
- For inducing a female Chinese alligator to bellow in an airtight chamber filled with helium-enriched air.
2019
Chemistry
- Watanabe Shigeru and others
- For estimating the total saliva volume produced per day by a typical five-year-old child.
2018
Medical education
- Horiuchi Akira
- For the medical report “Colonoscopy in the Sitting Position: Lessons Learned From Self-Colonoscopy.”
2017
Biology
- Yoshizawa Kazunori and Kamimura Yoshitaka
- For their discovery of a female penis, and a male vagina, in a cave insect.
2016
Perception
- Higashiyama Atsuki
- For investigating whether things look different when you bend over and view them between your legs.
2015
Medicine
- Kimata Hajime
- For experiments to study the biomedical benefits or biomedical consequences of intense kissing (and other intimate, interpersonal activities).
2014
Physics
- Mabuchi Kiyoshi and others
- For measuring the amount of friction between a shoe and a banana skin, and between a banana skin and the floor, when a person steps on a banana skin that’s on the floor.
2013
Chemistry
- Imai Shinsuke and others
- For discovering that the biochemical process by which onions make people cry is even more complicated than scientists previously realized.
2013
Medicine
- Niimi Masanori and others
- For assessing the effect of listening to opera, on heart transplant patients who are mice.
2012
Acoustics
- Kurihara Kazutaka and Tsukada Kōji
- For creating the SpeechJammer — a machine that disrupts a person’s speech, by making them hear their own spoken words at a very slight delay.
2011
Chemistry
- Imai Makoto and others
- For determining the ideal density of airborne wasabi (pungent horseradish) to awaken sleeping people in case of a fire or other emergency, and for applying this knowledge to invent the wasabi alarm.
2010
Transportation planning
- Nakagaki Toshiyuki and others
- For using slime mold to determine the optimal routes for railroad tracks.
2009
Biology
- Taguchi Fumiaki
- For demonstrating that kitchen refuse can be reduced more than 90% in mass by using bacteria extracted from the feces of giant pandas.
2008
Cognitive science
- Nakagaki Toshiyuki and others
- For discovering that slime molds can solve puzzles.
2007
Chemistry
- Yamamoto Mayu
- For developing a way to extract vanillin — vanilla fragrance and flavoring — from cow dung.
2005
Nutrition
- Nakamatsu Yoshirō
- For photographing and retrospectively analyzing every meal he has consumed during a period of 34 years (and counting).
2005
Biology
- Hayasaka Yōji
- For painstakingly smelling and cataloging the peculiar odors produced by 131 different species of frogs when the frogs were feeling stressed.
2004
Peace
- Inoue Daisuke
- For inventing karaoke, thereby providing an entirely new way for people to learn to tolerate each other.
2003
Chemistry
- Hirose Yukio
- For his chemical investigation of a bronze statue, in the city of Kanazawa, that fails to attract pigeons.
2002
Peace
- Satō Keita, Suzuki Matsumi, and Kogure Norio
- For promoting peace and harmony between the species by inventing Bowlingual, a computer-based automatic dog-to-human language translation device.
1999
Chemistry
- Makino Takeshi
- For his involvement with S-Check, an infidelity detection spray that wives can apply to their husbands’ underwear.
1997
Economics
- Maita Aki and Yokoi Akihiro
- For diverting millions of person-hours of work into the husbandry of Tamagotchi virtual pets.
1997
Biology
- Yagyū Takami and others
- For measuring people’s brainwave patterns while they chewed different flavors of gum.
1996
Biodiversity
- Okamura Chōnosuke
- For discovering the fossils of dinosaurs, horses, dragons, princesses, and more than 1,000 other extinct “mini-species,” each of which is less than 1/100 of an inch in length.
1995
Psychology
- Watanabe Shigeru and others
- For their success in training pigeons to discriminate between the paintings of Picasso and those of Monet.
1992
Medicine
- Kanda Fujihiro and others
- For their pioneering research study “Elucidation of Chemical Compounds Responsible for Foot Malodor,” especially for their conclusion that people who think they have foot odor do, and those who don’t, don’t.
Created by Nippon.com based on data from Improbable.com.
(Originally published in Japanese. Banner photo: Takebe Takanori and colleagues receiving the Ig Nobel Physiology Prize at the September 2024 ceremony at the MIT Museum. © Jiji.)